Data is growing at astonishing rates, it is being created every second. In 2020, every person will generate 1.7 megabytes every second. This data is powerful, it helps in making data-informed decisions. For example, Netflix saves $1 billion per year on customer retention, they use data to create its strategy to lower subscription cancellation rates by adjusting or adding new features.
Data generated is most often in a very raw format and it’s very hard to make sense of it. Which is why we need to process it to get more sophisticated information out of it. Data Mining is the process of extracting information from a large amount of data. Given data of ample size and quality, data mining provides the following capabilities:
- Predictive: Predict trends and behaviours.
- Desciptive: Discover unknown patterns.
Tasks
The data mining process involves 6 common classes of tasks:
- Anomaly Detection
- Association Rule Learning
- Clustering
- Classification
- Regression
- Summarization
1. Anomaly Detection

The process to recognize unusual data records, that might be an outlier/change/deviation/noise/error that requires further examination. This process is also used in a variety of domains, such as intrusion detection, fraud detection, fault detection, system health monitoring, event detection in sensor networks and detecting ecosystem disturbances.
2. Association Rule Learning

it is used to discover relationships between data variables to create a dependency model. The most popular example is affinity analysis or market basket analysis, let’s say from the store data we can determine which product or combination of products are frequently bought together, we can use this information for promotional pricing, product placements or marketing. It is also used for web usage mining, continuous production and bioinformatics.
3. Clustering

The task of grouping data which is in some way or another “similar”, without using known structures in the data. It is many fields, including machine learning, pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, and computer graphics.
4. Classification
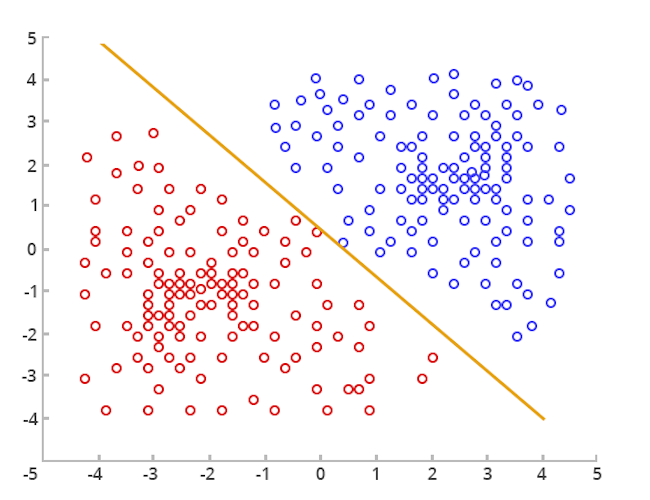
The task of mapping new or existing data into a set of categories, based on the features of data. Applications of classification are in domains like computer vision, drug discovery and development, geostatistics, speech recognition, statistical NLP, pattern recognition, recommender system etc.
5. Regression

It is a task to find a function which models the data with least error. It is to estimate the relationships between dependent variables (outcome variables) and one or more independent variables(predictors or features). It is used for sales/market forecasts, risk analysis for investments, quality control, human resources.
6. Summarization

Different visualizations used in summarization. Source:Morphocode
It is a task of providing a more compact representation of the data set, including visualization and report generation.
Architecture

This is the standard data mining architecture. Source: ResearchGate
1. Knowledge Base
This is the domain knowledge that is used to guide the search or evaluate the interestingness of resulting patterns.
2. Data Mining Engine
This is essential to the data mining system and ideally consists of a set of functional modules for tasks such as characterization, association and correlation analysis, classification, prediction, cluster analysis, outlier analysis, and evolution analysis.
3. Pattern Evaluation Module
This component typically employs interestingness measures interacts with the data mining modules to focus the search toward interesting patterns. It may use interestingness thresholds to filter out discovered patterns. Alternatively, the pattern evaluation module may be integrated with the mining module, depending on the implementation of the data mining method used. For efficient data mining, it is highly recommended to push the evaluation of pattern interestingness as deep as possible into the mining process to confine the search to only the interesting patterns.
4. User Interface
This module communicates between users and the data mining system, allowing the user to interact with the system by specifying a data mining query or task, providing information to help focus the search, and performing exploratory data mining based on the intermediate data mining results. Also, this component allows the user to browse database and data warehouse schemas or data structures, evaluate mined patterns, and visualize the patterns in different forms.
Process
Data mining is a process of discovering various models, summaries, and derived values from a given collection of data. The general experimental procedure adapted to data-mining problems involves the following steps:

Source: DigitalTransformationPro
Classification of Data Mining Systems
Data mining is an interdisciplinary field, the confluence of a set of disciplines, including database systems, statistics, machine learning, visualization, and information science.